Do the Sony A1 and the A7S III have THE SAME SENSOR?
That’s ridiculous (you say); one has 50MP the other has 12MP. But wait…

The best camera deals, reviews, product advice, and unmissable photography news, direct to your inbox!
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
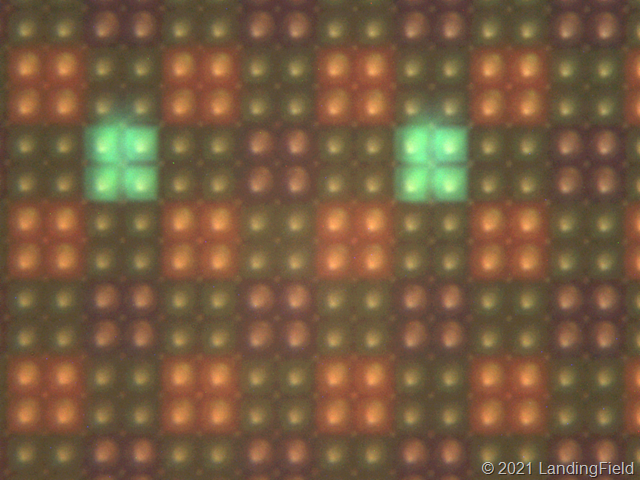
A teardown of a damaged Sony A7S III sensor by astrophotography site Landingfield and a subsequent examination under a microscope appears to show the A7S III sensor uses groups of four photosites to create each ‘pixel’ on the A7S III sensor. According to Landingfield, the sensor actually has 48 million effective pixels.
This process is known as ‘pixel binning’. By combining the light values from four small photosites you can get the effect off a single larger (and more sensitive) one. It’s used widely in the latest camera phones, may of which have sensors with 4x the actual photosites as the pixels in the final image.
It’s also used by some cameras for capturing video where the sensor resolution is far higher than that needed for video. However, most camera makers prefer ‘oversampling’ if possible and 'pixel binning' is a bit of a dirty word.
Oversampling vs pixel binning
With oversampling, the camera captures video at the full sensor resolution and downsizes it on-the-fly to create 4K video. This has the side effect of increasing sharpness and visual quality, which is why camera makers and videographers like it.
However, oversampling uses a LOT of processing power, so that while oversampling 6K capture down to 4K is feasible for many modern cameras, oversampling 8K down to 4K is too big a step – for the Sony A1, at least.
So on the Sony A1, you have a choice for 4K video capture. For best quality, you can swap to the smaller Super35 crop mode and capture 5.8K oversampled video to generate your 4K footage, but this crop factor means your effective focal length grows longer and your lens’s angle of view is reduced.
The alternative is to shoot ‘full width’ 4K footage with no crop, but since Sony doesn’t mention oversampling in this context, we take this to mean it uses pixel binning instead, combining sets of four pixels to create one ‘big’ one. The A1’s 50MP sensor is perfect for 4x pixel binning to get full-width 4K video (it’s very close to the 48MP technically required). It’s also exactly how the Sony A7S III sensor appears to be wired, according to Landingfield.
The best camera deals, reviews, product advice, and unmissable photography news, direct to your inbox!
So is it the same sensor?
So here’s how it looks to us. The Sony A1 offers full-width 4K capture with pixel binning from 48 million photosites. The Sony A7S III appears to do exactly the same.
No doubt the A7S III sensor is hard-wired completely differently and, even if all this is correct, Sony will still say, quite reasonably, that it’s a different sensor. Nevertheless, we wonder if both cameras are using the same stacked 48/50MP BSI sensor construction, but in the A7S III it’s hard-wired for pixel binning?
So what does it matter if the Sony A7S III uses 12 million photosites or 48 million pixel-binned down to 12? Probably very little. But, if true, that would be somewhat ironic given that Sony has for years been championing the quality of its oversampled video capture versus – ugh! – pixel binning.

Rod is an independent photography journalist and editor, and a long-standing Digital Camera World contributor, having previously worked as Group Reviews Editor, Head of Testing for the photography division, Technique Editor on N-Photo, and Camera Channel editor on TechRadar, as well as contributing to many other publications.
He has been writing about digital cameras since they first appeared, and before that began his career writing about film photography. He has used and reviewed practically every interchangeable lens camera launched in the past 20 years, from entry-level DSLRs to medium format cameras.
Rod has his own camera gear blog at fotovolo.com but also writes about photo-editing applications and techniques at lifeafterphotoshop.com.

